Thermal reliability of pcb circuit board can not be ignored
PCB manufacturers, PCB designers and PCBA manufacturers explain that the thermal reliability of PCB PCB cannot be ignored
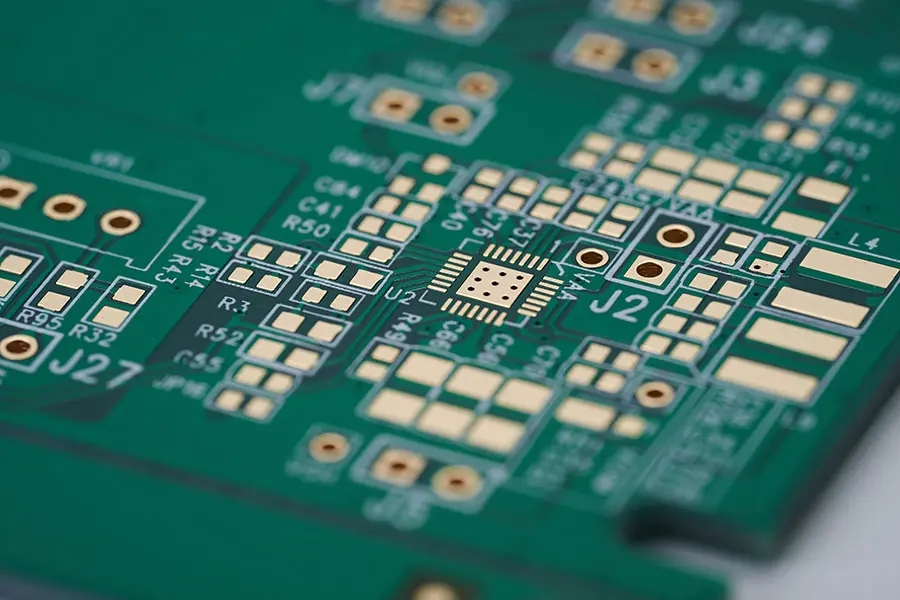
In general, the copper foil distribution on pcb circuit board is very complex, and it is diffICult to accurately model. Therefore, it is necessary to SIMplify the shape of the wiring when modeling. The electronIC components on the circuit board of the ANSYS model circuit board that is as close as possible to the actual circuit board can also be simulated by using the simplified modeling, such as MOS tubes, integrated circuit blocks, etc.

1. Thermal analysis
Thermal analysis during chip mounting can help designers to determine the electrical performance of components on PCB circuit boards, and help designers to determine whether components or circuit boards will be burned out due to high temperature. Simple thermal analysis is only to calculate the average temperature of the circuit board, and complex thermal analysis is to establish a transient model for Electronic devices with multiple circuit boards. The accuracy of thermal analysis ultimately depends on the accuracy of component power consumption provided by circuit board designers.
In many applications, weight and physical size are very important. If the actual power consumption of components is very SMAll, the design safety factor may be too high, so that the circuit board design uses the component power consumption value that is inconsistent with the actual or too conservative as the basis for thermal analysis. On the contrary (and more seriously), the design of thermal safety factor is too low, that is, the temperature of components in actual operation is higher than what analysts predicted. Such problems are generally solved by installing heat dissipation devices or fans to cool the circuit board. These external accessories increase the cost and prolong the time. The addition of fans in the design will also bring instability to the reliability. Therefore, active rather than passive cooling methods (such as natural convection, conduction and radiation cooling) are mainly used for PCB.
2. Simplified modeling of circuit board
Before modeling, analyze the main heating devices in the circuit board, such as MOS tubes and integrated circuit blocks, which convert most of the lost power into heat when working. Therefore, these devices need to be considered when modeling. In addition, consider the copper foil on the circuit board substrate as the conductor coating. They not only conduct electricity, but also conduct heat in the design. Their thermal conductivity and heat transfer area are relatively large. The circuit board is an indispensable part of the electronic circuit. Its structure is composed of epoxy resin substrate and copper foil coated as a conductor. The thickness of epoxy resin substrate is 4mm, and the thickness of copper foil is 0.1mm. The thermal conductivity of copper is 400W/(m ℃), while that of epoxy resin is only 0.276W/(m ℃). Although the added copper foil is very thin and thin, it has a strong guiding effect on heat, so it cannot be ignored in modeling. PCB manufacturers, PCB designers and PCBA manufacturers explain that the thermal reliability of PCB can not be ignored