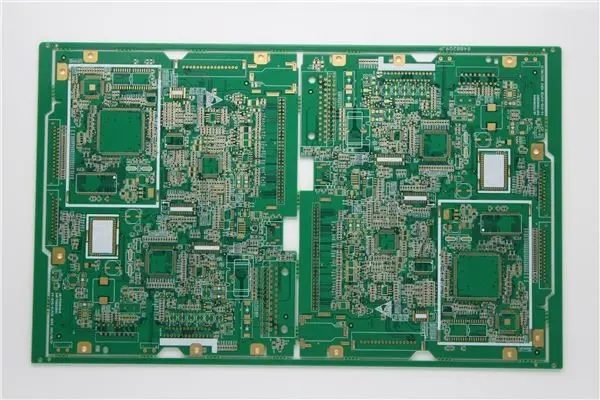
DetaiLED explanation of BGA repair and ball planting process
1: Rework of ordinary SMD
The principle of the common SMD repair system: the hot gas flow is gathered on the pins and pads of surface mount devices (SMD) to melt the solder joints or reflow the solder paste to complete the disassembly and welding functions.
The difference between repair systems from different manufacturers is mainly due to different heating sources or different hot air flow modes. Some nozzles make hot air above the SMD. From the perspective of protecting components, it is better to choose the air flow around the PCB. In order to prevent PCB warping, a repair system with the function of preheating the PCB should also be selected.
2: BGA repair
Repair steps of BGA with HT996:
1: Removing BGA
Use a soldering iron to clean and level the residual soldering tin on the PCB pad. Use a solderless braided tape and a flat spade soldering iron head for cleaning. Be careful not to damage the pad and solder mask during operation.
Clean the flux residue with special cleaning agent.
2: DehumidifICation treatment
Because PBGA is sensitive to moisture, check whether the device is affected with moisture before assembly, and remove moisture from the affected device.
3: Printing solder paste
Because other components have been installed on the surface assembly board, the special SMAll template BGA must be used. The template thickness and opening size should be determined according to the ball diameter and ball distance. After printing, the printing quality must be checked. If the PCB is unqualified, it must be cleaned and dried before printing again. For C SP with a ball pitch of less than 0.4 mm, it is not necessary to print solder paste, so it is not necessary to process the template for repair, and directly paint paste flux on the PCB pad. Put the PCB to be disassembled into the welding furnace, press the reflow key, wait until the machine is finished according to the set program, press the In/Out key at the highest temperature, use the vacuum suction pen to remove the components to be disassembled, and then the PCB can be cooled.
4: Cleaning pads
Use a soldering iron to clean and level the residual soldering tin on the PCB pad. Use a solder strip and a flat spade soldering iron to clean it. Be careful not to damage the pad and solder mask during operation.
5: Dehumidification treatment
Because PBGA is sensitive to moisture, check whether the device is affected with moisture before assembly, and remove moisture from the affected device.
6: Printing solder paste
Because other components have been installed on the surface assembly board, the special small template BGA must be used. The template thickness and opening size should be determined according to the ball diameter and ball distance. After printing, the printing quality must be checked. If the PCB is unqualified, it must be cleaned and dried before printing again. For CSP with a ball pitch of less than 0.4 mm, solder paste can be not printed, so it is not necessary to process the template for repair, and paste flux can be directly applied on the PCB pad.

7: Paste BGA
If it is a new BGA, it must be checked whether it is affected with moisture. If it is already affected with moisture, it should be removed with moisture treatment before mounting.
The removed BGA device can be reused generally, but it can only be used after ball planting. The steps for mounting BGA devices are as follows:
A: Place the surface assembly plate printed with solder paste on the workbench
B: Select an appropriate suction nozzle and turn on the vacuum pump. Suck up the BGA device, move the suction nozzle downward after the bottom of the BGA device completely coincides with the PCB pad, mount the BGA device on the PCB, and then turn off the vacuum pump.
8: Reflow welding
The welding temperature can be set according to the device size, PCB thickness and other specific conditions. The welding temperature of BGA is about 15 degrees higher than that of traditional SMD.
9: Inspection
The welding quality inspection of BGA requires X-ray or ultrasonic inspection equipment. If there is no inspection equipment, the welding quality can be judged by functional test or inspected by experience.
Lift up the surface assembly board of the welded BGA, and look at the periphery of the BGA to see whether it is transparent, whether the distance between the periphery of the BGA and the PCB is consistent, whether the solder paste is completely melted, whether the shape of the solder ball is correct, and how the solder ball collapses.
If it is opaque, it indicates that there is bridge or solder ball between solder balls;
If the shape of the solder ball is not correct and there is distortion, it indicates that the temperature is not enough, the welding is not sufficient, and the self positioning effect is not fully exerted when the solder flows again;
Solder ball collapse degree: the collapse degree is related to welding temperature, solder paste amount and pad size. If the pad design is reasonable, the distance between the BGA bottom and PCB after reflow soldering is 1/5-1/3 lower than that before soldering. If the welding ball collapses too much, it indicates that the temperature is too high and bridging is easy to occur.
If the distance between BGA and PCB is inconsistent, the temperature around BGA is uneven.
3: BGA planting ball
1: Remove the residual solder on the BGA bottom pad and clean it
Use a soldering iron to clean and level the residual soldering tin on the PCB pad, which can be cleaned with a solderless braided tape and a flat spade soldering iron head. Be careful not to damage the pad and solder mask during operation.
Clean the flux residue with special cleaning agent.
2: Printing flux on BGA bottom pad
Generally, high adhesion flux is used to play the role of bonding and soldering. It should be ensured that the flux pattern is clear and does not overflow after printing. Sometimes, solder paste can be used instead. When solder paste is used, the metal components of the solder paste should match the metal components of the solder ball.
BGA special small template shall be used for printing. The template thickness and opening size shall be determined according to the ball diameter and ball distance. After printing, the printing quality must be checked. If it is unqualified, it must be cleaned before printing again.
3: Select solder ball
The material and diameter of the welding ball shall be considered when selecting the welding ball. At present, the solder paste material of PBGA solder ball is generally 63Sn/37Pb, which is consistent with the current reflow soldering material. Therefore, the solder ball that is consistent with the BGA device solder ball material must be selected.
The selection of solder ball size is also important. If high viscosity flux is used, the solder ball with the same diameter as the BGA device solder ball should be selected; If the solder paste is used, the solder ball with a smaller diameter than the BGA device solder ball shall be selected.
4: Ball planting
A) Adopt the ball planter method
If there is a ball planter, select a template that matches the BGA pad. The opening size of the template should be 0.05-0.1mm larger than the diameter of the solder ball. Spread the solder ball evenly on the template, shake the ball planter, roll the surplus solder ball from the template to the solder ball collecting slot of the ball planter, so that the surface of the template is exactly one solder ball in each leak.
Place the ball planter on the workbench, suck the BGA device printed with flux or solder paste onto the suction nozzle, align it according to the method of pasting BGA, move the suction nozzle downward, paste the BGA device onto the solder ball on the surface of the ball planter template, then suck up the BGA device, and stick the solder ball to the corresponding pad of the BGA device with the aid of the viscosity of the flux or solder paste. Clamp the outer frame of the BGA device with tweezers, turn off the vacuum pump, place the solder ball of the BGA device on the workbench facing upwards, check if there is any missing solder ball, and if there is, use tweezers to make up.
B) Adopt template method
Place the BGA device printed with flux or solder paste on the workbench, with the flux or solder paste facing upward. Prepare a template matching the BGA bonding pad. The opening size of the template should be 0.05~0.1 ㎜ larger than the diameter of the solder ball. Use a cushion block to stand high around the template and place it above the BGA device printed with flux or solder paste, so that the distance between the template and BGA is equal to or slightly less than the diameter of the solder ball, and align it under the microscope. Spread the welding ball evenly on the template, pull (remove) the surplus welding ball with tweezers, so that a welding ball is reserved in each leakage hole on the template surface. Remove the formwork, check and supplement it.
C) Manual mounting
Place the BGA device printed with flux or solder paste on the workbench, with the flux or solder paste facing upward. Place the solder balls one by one with tweezers or suction pen just like the patch.
D) Brush appropriate amount of solder paste
When processing the template, thicken the template thickness, slightly enlarge the opening size of the template, and directly print the solder paste on the bonding pad of BGA. Due to the effect of surface tension, solder balls are formed after reflow welding.
5: Reflow welding
After reflow soldering, the solder ball is fixed on the BGA device.
6: After welding
After the ball planting process is completed, the BGA device should be cleaned and mounted and welded as soon as possible to prevent oxidation of the ball and moisture of the device.