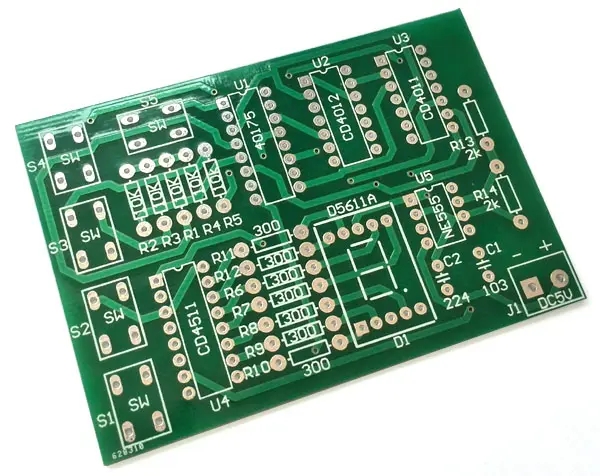
BasIC principles and requirements of PCB drawing design
1. The design of the printed circuit board starts from the determination of the size of the board. Because the size of the printed circuit board is limited by the size of the chassis shell, it is appropriate to fit it into the shell. Secondly, the connection mode between the printed circuit board and external components (mainly potentiometers, sockets or other printed circuit boards) should be considered. The printed circuit board and external components are generally connected by plastic wires or metal isolation wires. But sometimes it is also designed as a socket. Namely, when installing a plug-in printed circuit board in the equipment, the contact position that acts as the socket shall be reserved. For larger components instalLED on the printed circuit board, metal accessories shall be added for fixation to improve the vibration resistance and impact resistance.

2. Basic method of wiring diagram design
First of all, you need to have a complete understanding of the specifications, dimensions, areas, etc. of the selected components and various sockets; Reasonable and careful consideration shall be given to the location arrangement of each component, mainly from the perspective of electromagnetic compatibility, anti-interference, short routing, less crossing, power supply, ground path and decoupling. After the location of each component is determined, it is the online connection of each component. The relevant pins are connected according to the circuit diagram. There are many ways to complete the connection. There are two ways to design the printed circuit diagram: computer aided design and manual design.
The most original is to arrange the layout manually. This is rather laborious, and it often needs to be repeated several times before it can be finally completed. This can also be done when there is no other drawing equipment. This manual layout method is also very helpful for designers who are just learning the printed board drawing. There are many kinds of computer aided drawing software with different functions, but generally speaking, it is convenient to draw and modify, and can be saved, stored and printed.
Next, determine the required size of the PCB, and preliminarily determine the position of each component according to the schematic diagram, and then continuously adjust to make the layout more reasonable. The wiring arrangement between components in the PCB is as follows:
(1) Cross circuits are not allowed in printed circuits. Lines that may cross can be solved by "drilling" or "winding". That is to say, let a lead "drill" through the gap at the foot of other resistors, capacitors, and transistors, or "wind" through one end of a lead that may cross. Under special circumstances, how to make the circuit very complex? In order to SIMplify the design, it is also allowed to use a wire jumper to solve the cross circuit problem.
(2) Resistance, diode, tubular capacitor and other components can be installed in "vertical" and "horizontal" modes. Vertical refers to the installation and welding of components perpendicular to the circuit board, which has the advantage of saving space. Horizontal refers to the installation and welding of components parallel to and close to the circuit board, which has the advantage of good mechanical strength for component installation. For these two different mounting components, the component hole spacing on the printed circuit board is different.
(3) The grounding point of the circuit at the same level shall be as close as possible, and the power filter capacitor of the circuit at this level shall also be connected to the grounding point at this level. In particular, the ground points of the base and EMItter of the current transistor cannot be too far away, otherwise the copper foil between the two ground points will be too long, which will cause interference and self excitation. The circuit using this "one point grounding method" will work more stably and is not easy to self excitation.
(4) The general grounding wire must be arranged in the order from weak current to strong current in a high frequency medium frequency low frequency level. It is not allowed to randomly turn over and over. It is better to have a long connection between levels, but also to comply with this provision. In particular, the grounding wire arrangement of frequency converter head, regeneration head and frequency converter head is more strict. If it is improper, self excitation will occur and it will not work.
High frequency circuits such as FM head often use a large area of enclosed ground wire to ensure a good shielding effect.
(5) Strong current leads (common ground wire, power amplifier power lead, etc.) should be as wide as possible to reduce wiring resistance and its voltage drop, and reduce self excitation caused by parasitic coupling.
(6) The route with high impedance shall be as short as possible, and the route with low impedance may be longer, because the route with high impedance is easy to whistle and absorb signals, causing circuit instability. The power line, ground wire, base wire without feedback component, emitter wire, etc. are all low impedance wires. The base wire of the emitter follower and the ground wire of the two audio channels of the radio recorder must be separated and formed into one circuit respectively until the end of the function. If the two ground wires are connected, it is very easy to produce crosstalk and reduce the separation.
The following points should be noted in PCB design
1. Wiring direction: from the welding surface, the arrangement direction of the components should be consistent with the schematic diagram as much as possible, and the wiring direction should be consistent with the wiring direction of the circuit diagram. Since it is usually necessary to detect various parameters on the welding surface during the production process, this is convenient for inspection, debugging and maintenance in production (Note: it refers to the premise of meeting the requirements of circuit performance, complete machine installation and panel layout).
2. All PCB components shall be arranged and distributed reasonably and evenly, striving for neat, beautiful and rigorous structure.
3. The placement mode of resistance and diode: horizontal and vertical:
(1) Horizontal placement: When the number of circuit components is SMAll and the size of the circuit board is large, it is generally better to use horizontal placement; When the resistance below 1/4W is placed horizontally, the distance between two pads is generally 4/10 inches, and when the resistance below 1/2W is placed horizontally, the distance between two pads is generally 5/10 inches; When the diode is laid horizontally, 1N400X series rectifier tube is generally 3/10 inch; 1N540X series rectifier tube, generally 4~5/10 inches.
(2) Vertical placement: When the number of circuit components is large and the size of the circuit board is small, vertical placement is generally adopted. The spacing between two pads is generally 1~2/10 inches.
4. Potentiometer: placement principle of IC base
(1) Potentiometer: it is used to adjust the output voltage in the voltage regulator. Therefore, the design of the potentiometer should increase the output voltage when it is fully adjusted clockwise, and decrease the output voltage when it is adjusted counterclockwise; In the adjustable constant current charger, the potentiometer is used to adjust the charging current fold. When the potentiometer is designed to be full and adjusted clockwise, the current will increase.
The position of the potentiometer should meet the requirements of the whole machine structure installation and panel layout, so it should be placed at the edge of the board as far as possible, with the rotary handle facing outward.
(2) IC base: When designing the printed board drawing, when using the IC base, pay special attention to whether the positioning slot on the IC base is placed in the correct direction, and whether each IC pin position is correct. For example, the first pin can only be located at the lower right corner or upper left corner of the IC base, and close to the positioning slot (from the welding surface).
5. Arrangement of incoming and outgoing terminals
(1) The distance between the two associated lead ends should not be too large, generally about 2-3/10 inches.
(2) The incoming and outgoing line ends shall be concentrated on 1 to 2 sides as far as possible, and shall not be too discrete.
6. When designing the PCB wiring diagram, pay attention to the pin arrangement order, and the component pin spacing should be reasonable.
7. On the premise of ensuring the circuit performance requirements, the design shall strive for reasonable wiring, less use of external jumper, and wiring shall be carried out according to certain charging requirements, so as to be intuitive, convenient for installation, height and maintenance.
8. When designing the wiring diagram, the routing shall be as simple and clear as possible.
9. PCB layout line width and line spacing shall be moderate, and the spacing between two bonding pads of capacitor shall be consistent with the spacing between capacitor lead pins as far as possible;
10. PCB design shall be carried out in a certain order, such as from left to right and from top to bottom.