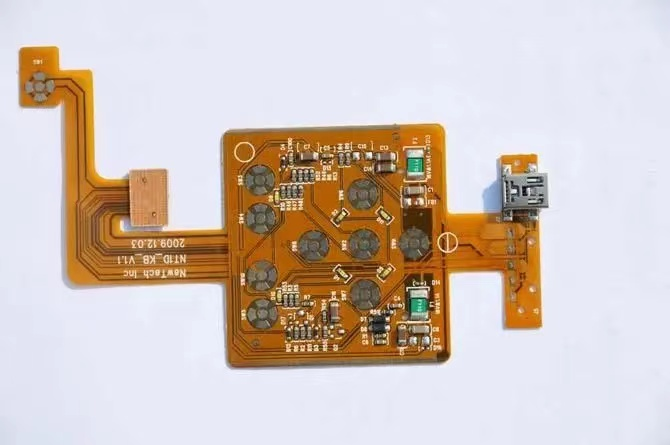
FPC circuit board - basIC structure copper foil substrate (CopperFilm)
Copper foil: basically divided into electrolytic copper and calendered copper. The common thickness is 1oz1/2oz and 1/3oz
Substrate film: the common thickness is 1mil and 1/2mil
Glue (adhesive): the thickness depends on the customer's requirements
CoverFilm
Protective film of covering film: used for surface insulation. The common thickness is 1mil and 1/2mil
Glue (adhesive): the thickness depends on the customer's requirements
Release paper: avoid the adhesive adhering to foreign matters before pressing; It is convenient for operation
PIStiffenerFilm
Reinforcing plate: It is used to strengthen the mechanical strength of FPC, which is convenient for surface installation. The common thickness is 3mil to 9mil
Glue (adhesive): the thickness depends on the customer's requirements
Release paper: Avoid foreign matters on the adhesive before pressing
EMI: electromagnetic shielding film, which protects the circuit in the circuit board from external interference (strong electromagnetic area or easily interfered area).
In the structure of flexible circuit,FPC is composed of thin film, adhesive and conductor.
Marginal film
The bottom edge film forms the base layer of the circuit, and the copper foil is bonded to the bottom edge layer by the adhesive. In a multilayer design, it is then bonded to the inner layer. They are also used as protective coverings to isolate the circuit from dust and moisture, and to reduce stress during flexure. The copper foil forms a conductive layer.
In some flexible circuits, rigid components made of aluminum or stainless steel are used, which can provide dimensional stability, physical support for the placement of components and wires, and stress relief. The adhesive bonds the rigid member and the flexible circuit together. In addition, another material is sometimes used in flexible circuits. It is a bonding layer, which is formed by coating adhesive on both sides of the edge film. The adhesive layer provides environmental protection and electronic edge breaking functions, and can eliminate a layer of film, and has the ability to bond multiple layers with fewer layers.
There are many kinds of thin film materials, but the most commonly used are polyimide and polyester materials. At present, nearly 80% of all flexible circuit manufacturers in the United States use polyimide film materials, and about 20% use polyester film materials. Polyimide material is nonflammable, has stable geometric dimensions, has high tensile strength, and has the ability to withstand welding temperature. Polyester, also known as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), has SIMilar physical properties to polyimide, has low dielectric constant, absorbs little moisture, but is not resistant to high temperature.
The melting point of polyester is 250 ℃, and the glass transition temperature (Tg) is 80 ℃, which limits their use in applications requiring a large number of end welding. They are rigid in cryogenic applications. Nevertheless, they are suitable for use on products such as telephones and other products that do not need to be exposed to harsh environments.
Polyimide film is usually combined with polyimide or acrylic adhesive, while polyester film is generally combined with polyester adhesive. The advantages of combining with materials with the same characteristics can ensure dimensional stability after dry welding or after multiple laminating cycles. Other important characteristics of adhesives are low dielectric constant, high marginal resistance, high glass transition temperature (Tg) and low moisture absorption.
Adhesive
In addition to being used for bonding the thin film to the conductive material, the adhesive can also be used as a coating, a protective coating, and a covering coating. The main difference between the two lies in the application mode used. The purpose of bonding the covering layer to cover the edge film is to form a circuit with a laminated structure. Screen printing technology used for covering and coating adhesive.
Not all laminated structures contain adhesives, and layers without adhesives form thinner circuits and greater flexibility. It has better thermal conductivity compared with the adhesive based laminated structure. Due to the thin structure of the adhesive free flexible circuit and the elimination of the thermal resistance of the adhesive, the thermal conductivity is improved. It can be used in the working environment where the FPC circuit based on the adhesive laminated structure cannot be used.
conductor
Copper foil is suitable for use in FPC circuits. It can be Electrodeposited or plated. One side of the copper foil prepared by electrodeposition is glossy, while the other side is dull and lusterless. It is a flexible material and can be made into various thicknesses and widths. The matt side of ED copper foil is often treated specially to improve its adhesion. In addition to flexibility, forged copper foil also has the characteristics of hard and smooth. It is suitable for applications requiring dynamic bending.