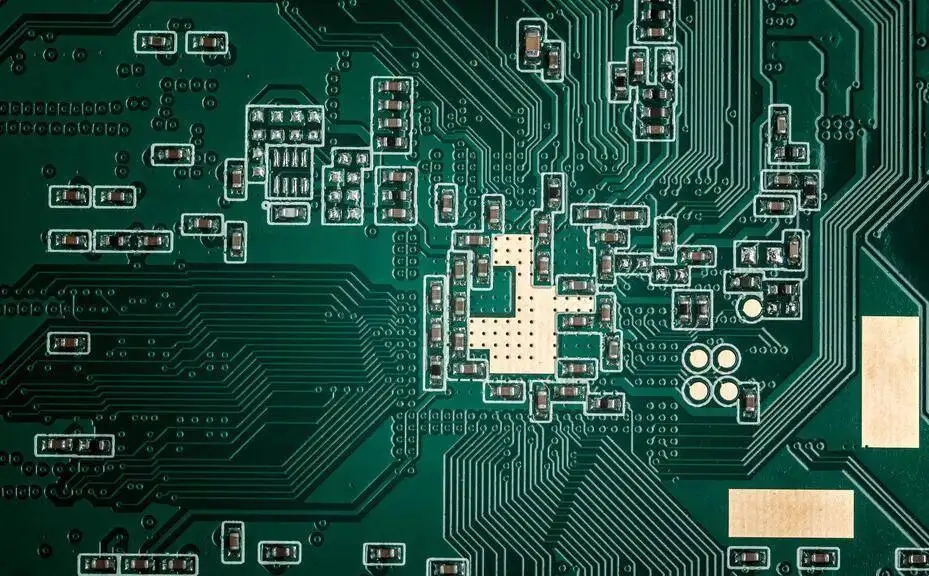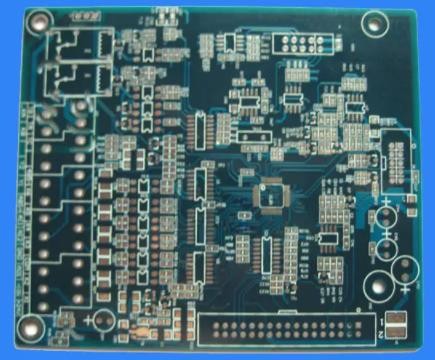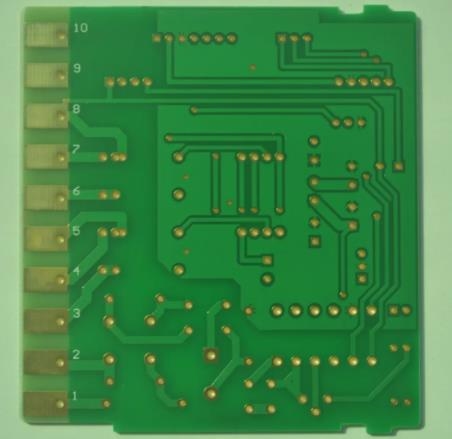
Printed circuit board (PCB) appears in almost every kind of electronIC equipment. If there are electronIC parts in a certain device, they are also embedded in PCB of different sizes. In addition to fixing various SMAll parts, the main function of the PCB is to provide the electrical connection between the upper parts. As electronic equipment becomes more and more complex, more and more parts are needed, and the lines and parts on PCB become more and more intensive. A standard PCB looks like this. The bare board (with no parts on it) is also often calLED "Printed Wiring Board (PWB)".
The base plate of the board itself is made of insulating and heat-insulating materials that are not easy to bend. The small circuit material visible on the surface is copper foil. Originally, the copper foil was covered on the whole board, but part of it was etched during the manufacturing process, and the left part beCAMe a small network circuit. These lines are called conductor patterns or wiring, and are used to provide circuit connections for parts on a PCB.
To fix the parts on the PCB, we directly solder their pins on the wiring. On the most basic PCB (single panel), parts are concentrated on one side, and wires are concentrated on the other side. In this way, we need to drill holes in the board so that the pins can pass through the board to the other side, so the pins of the parts are welded on the other side. Because of this, the front and back sides of PCB are called component side and solder side respectively.

If there are some parts on the PCB that can be removed or installed back after fabrication, the socket will be used when installing the parts. Because the socket is directly welded to the board, the parts can be disassembled at will. The following is a ZIF (Zero Insertion Force) socket, which allows parts (here referred to as CPU) to be easily inserted into or removed from the socket. The fixing rod beside the socket can be fixed after you insert the part.
If two PCBs are to be connected with each other, we usually use the edge connector commonly known as "golden finger". The gold finger contains many bare copper pads, which are actually part of PCB wiring. Usually, when connecting, we insert the golden finger on one PCB into the appropriate slot on the other PCB (generally called expansion slot Slot). In computers, such as display cards, sound cards or other SIMilar interface cards, are connected to the motherboard by means of golden fingers.
Green or brown on PCB is the color of solder mask. This layer is an insulating protective layer, which can protect copper wires and prevent parts from being welded to incorrect places. A layer of silk screen will be printed on the solder mask. Usually, words and symbols (mostly white) will be printed on it to MARK the position of each part on the board. The screen printing surface is also called the icon surface.
Single Sided Boards
We just mentioned that on the most basic PCB, parts are concentrated on one side and wires are concentrated on the other side. Because the wires only appear on one side, we call this PCB single sided. Because there are many strict restrictions on the design circuit of a single panel (because there is only one side, and the wiring cannot cross and must go around a separate path), only early circuits use such boards.
Double Sided Boards
This circuit board has wiring on both sides. However, if you want to use two wires, you must have a proper circuit connection between them. This "bridge" between circuits is called a pilot hole (via). The pilot hole is a small hole filled with or coated with metal on the PCB,
It can be connected with wires on both sides. Because the area of the double-sided board is twice as large as that of the single panel, and because the wiring can be staggered (it can be wound to the other side), it is more suitable for circuits more complex than the single panel.
In order to increase the area that can be wired, more single or double sided wiring boards are used for multilayer boards. Several double-sided boards shall be used for Multilayer boards, and a layer of insulating layer shall be placed between each layer of boards and then glued (pressed). The number of layers of the board represents several independent wiring layers. Usually, the number of layers is even and includes the two outermost layers. Most motherboards are 4-8 layer structures, but technically, nearly 100 layers of PCB can be achieved. Most large supercomputers use multilayer mainboards. However, since such computers can already be replaced by clusters of many ordinary computers, super multilayer boards have been gradually eliminated. Because the layers in the PCB are closely combined, it is generally not easy to see the actual number. However, if you carefully observe the motherboard, you may see it.
If the guide hole (via) we just mentioned is applied to the double-sided board, it must pierce the whole board. However, in a multilayer board, if you only want to connect some of the circuits, the pilot hole may waste some circuit space in other layers. Buried vias and Blind vias can avoid this problem because they only penetrate several layers. The blind hole is used to connect several layers of internal PCBs and surface PCBs without penetrating the whole board. The embedded hole is only connected to the internal PCB, so it cannot be seen from the surface.
In a multilayer PCB, the whole layer is directly connected to the ground wire and power supply. So we classify each layer as Signal layer, Power layer or Ground layer. If parts on a PCB need different power supplies, such PCBs usually have more than two layers of power and wire layers. Part Packaging Technology
Through Hole Technology
Place the parts on one side of the board and weld the pins on the other side. This technology is called "Through Hole Technology (THT)" packaging. This type of part will take up a lot of space, and will need to drill a hole for each joint pin. So their pins actually take up space on both sides, and the solder joints are relatively large. On the other hand, THT parts are better connected with PCBs than SMT (Surface Mounted Technology) parts. We will talk about this later. For example, flat cable sockets and similar interfaces need to be pressure resistant, so they are usually THT packaged.
For parts using surface mounted technology (SMT), the pins are welded on the same side as the parts. This technology does not need to weld each pin, but drill holes in PCB.
Surface adhesive parts can even be welded on both sides.
SMT is also smaller than THT parts. Compared with PCBs using THT parts, PCBs using SMT technology are much denser. SMT package parts are also cheaper than THT's. Therefore, it is not surprising that most of today's PCBs are SMTs.
Because the solder joints and the pins of the parts are very small, it is very difficult to use manual welding. However, if we consider that the current assembly is fully automatic, this problem will only occur when repairing parts.
Design process
In PCB design, before formal wiring, there are still long steps to go through. The main design process is as follows:
System specifications
First of all, plan out the system specifications of the electronic equipment. It includes system functions, cost limits, size, operation conditions, etc. The function block diagram of the system must be made next. The relationship between squares must also be marked.
Split the system into several PCB
If the system is divided into several PCBs, it can not only reduce the size, but also enable the system to upgrade and exchange parts. The system function block diagram provides the basis for our segmentation. For example, a computer can be divided into a motherboard, a display card, a sound card, a floppy disk drive, a power supply, and so on. Determine the packaging method and the size of each PCB.
When the technology and the number of circuits used by each PCB are determined, the next step is to determine the size of the board. If the design is too large, the packaging technology will be changed or the segmentation will be performed again. When selecting technologies, the quality and speed of the circuit diagram should also be taken into account.
Draw the circuit overview of all PCBs
The interconnection details between parts shall be shown in the overview. PCB in all systems must be traced. Nowadays, most of them adopt CAD (Computer Aided Design). The following is an example of a design using CircuitMakerTM.
Circuit overview for PCB
Simulation operation of preliminary design
In order to ensure that the designed circuit diagram can work normally, it must first be simulated with computer software. This kind of software can read the design drawing and display the circuit operation in many ways. This is much more effective than actually making a sample PCB and then measuring it manually.
Place the part on the PCB
The placement of parts depends on how they are connected. They must be connected to the path in the most efficient way. The so-called efficient wiring means that the shorter the lead wire is and the fewer layers it passes through (which also reduces the number of guide holes), the better. However, we will mention this problem again during the actual wiring. The following is how the bus is wired on the PCB. In order to make all parts have perfect wiring, the placement position is very important.
Test wiring possibilities and correct operation at high speeds
Some of today's computer software can check whether the positions of various parts can be correctly connected, or whether they can operate correctly under high-speed operation. This step is called arranging parts, but we won't go into it too deeply. If there is a problem with the circuit design, you can also rearrange the position of the parts before exporting the circuit in the field.
Export circuit on PCB
The connections in the overview will now be wired in the field. This step is usually fully automatic, but in general, some parts need to be changed manually. The following is the wire template of the 2-layer board. The red and blue lines represent the part layer and welding layer of PCB respectively. The white text and the square represent the marks on the screen printing surface. Red dots and circles represent drill holes and pilot holes. On the far right, we can see that there are gold fingers on the welding surface of PCB. The final composition of this PCB is usually called Artwork.
Each design must comply with a set of regulations, such as the minimum reserved gap between lines, the minimum line width, and other similar actual restrictions. These provisions vary according to the speed of the circuit, the strength of the transmission signal, the sensitivity of the circuit to power consumption and noise, and the quality of the material and manufacturing equipment. If the current intensity rises, the thickness of the wire must also increase. In order to reduce the cost of PCB, while reducing the number of layers, it is also necessary to pay attention to whether these provisions are still met. If the structure of more than 2 layers is required, the power layer and ground layer are usually used to avoid the influence on the transmission signal on the signal layer, and can be used as the protective cover of the signal layer.
Wiring Rear Circuit Test
In order to ensure that the circuit can operate normally after the conductor, it must pass the final test. This test can also check whether there are incorrect connections, and all online connections follow the overview.
Establish production archives
Because there are many CAD tools for PCB design at present, the manufacturer must have a standard file to manufacture the board. There are several standard specifications, but the Gerber files specification is most commonly used. A group of Gerber files includes the plan of each signal, power supply and ground wire layer, the plan of solder mask layer and screen printing surface, and the designated files of drilling, taking and placing.