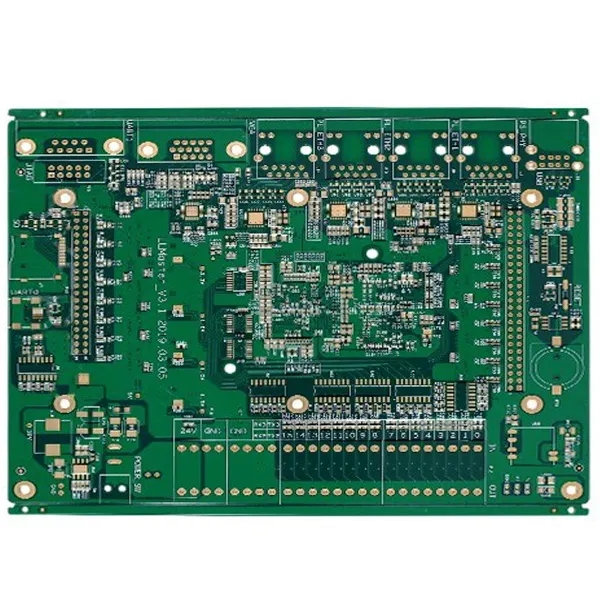
ElectronIC factory editor: explanation of classification of soft circuit boards
With the increasing output ratio of soft PCB and the application and promotion of rigid and flexible PCB, it is now common to add soft, rigid or rigid and Flexible PCBs when talking about PCBs. Generally, PCB made of soft insulating substrate is calLED soft PCB or flexible PCB, and rigid flexible composite PCB is called rigid flexible PCB. It meets the needs of today's electronic products to develop in the direction of high-density, high reliability, miniaturization and lightweight, and also meets the strict economic requirements and the needs of MARKet and technical competition.
In foreign countries, soft PCB has been widely used in the early 1960s. In China, production and application began in the mid-1960s. In recent years, with the promotion of global economic integration and open market and the introduction of technology, their use has been growing constantly. Some SMAll and medium-sized rigid PCB factories aim at this opportunity to adopt soft and hard manufacturing processes, improve tooling tools and processes by using existing equipment, transform the production of soft PCBs and adapt to the growing demand for soft PCB use. In order to further understand PCB, here is an exploratory introduction to soft PCB technology.
Classification of flexible circuit boards
1. Classification of soft PCB
Soft PCBs are generally classified as follows according to the number of layers and structure of conductors:
1.1 Single sided flexible PCB
A single-sided flexible PCB has only one layer of conductor, and the surface can be covered or not covered. The insulating substrate materials used vary with the application of products. The commonly used insulating materials are polyester, polyimide, polytetrafluoroethylene, soft epoxy glass cloth, etc.
Single sided flexible PCB can be further divided into the following four categories:
1) Unilaterally connected without covering
The wire pattern of this kind of flexible PCB is on the insulating substrate, and there is no covering layer on the wire surface. Like the common single-sided rigid PCB. This kind of product is the cheapest one and is usually used in non critical and environmental protection applications. The interconnection is realized by tin welding, fusion welding or pressure welding. It was often used in early telephone sets.
2) One side connected with covering layer
Compared with the former type, this type only has an additional layer of coating on the conductor surface according to the customer's requirements. The pad shall be exposed when covering, and it can be SIMply not covered in the end area. Clearance holes can be used if precision is required. It is one of the most widely used single-sided soft PCB, and is widely used in automotive instruments and electronic instruments.
3) Double sided without overlay
Such connectors can be connected on the front and back of the wire. In order to achieve this, a passage hole is opened on the insulating substrate at the bonding pad. This passage hole can be punched, etched or made by other mechanical methods at the required position of the insulating substrate. It is used for mounting elements and devices on both sides and where soldering is required. There is no insulating substrate in the pad area at the path. Such pad areas are usually removed by chEMIcal methods.
4) Double sided connection with covering layer
The difference between this type and the previous type is that there is a layer of coating on the surface. However, the covering layer has access holes, which can also be terminated on both sides and still maintain the covering layer. This kind of flexible PCB is made of two layers of insulating material and one layer of metal conductor. It is used in situations where the covering layer needs to be insulated from the surrounding devices, and the end needs to be connected to both the front and the back.

1.2 Double sided flexible PCB
Double sided flexible PCB with two layers of conductors. The application and advantages of this type of double-sided flexible PCB are the same as those of single-sided flexible PCB, and its main advantage is to increase the wiring density per unit area. The utility model can be divided into the following categories according to the presence or absence of metallized holes and the presence or absence of coatings: a. those without metallized holes or coatings; B There is no metallized hole and a covering layer; C There are metallized holes and no covering layer; D. There are metallized holes and coatings. Double sided soft PCB without covering layer is seldom used.
1.3 Multilayer soft PCB
Soft multilayer PCB Like rigid multilayer PCB, multi-layer lamination technology can be used to make multi-layer soft PCB. The simplest multilayer soft PCB is a three layer soft PCB formed by covering two layers of copper shielding layers on both sides of a single-sided PCB. The three-layer flexible PCB is equivalent to coaxial wire or shielded wire in electrical characteristics. The most commonly used multi-layer soft PCB structure is a four layer structure, which uses metallized holes to realize inter layer interconnection. The middle two layers are generally the power layer and the grounding layer.
The advantages of multilayer flexible PCB are that the substrate film is light in weight and has excellent electrical properties, such as low dielectric constant. Multilayer Flexible PCB board made of polyimide film is about 1/3 lighter than rigid epoxy glass cloth multilayer PCB board, but it loses the excellent flexibility of single-sided and double-sided flexible PCB. Most of these products do not require flexibility.
Multilayer flexible PCB can be further divided into the following types:
1) Multilayer PCB is formed on flexible insulating substrate, and its finished product is specified as flexible: this structure usually bonds the two ends of many single-sided or double-sided microstrip flexible PCBs together, but the center part is not bonded together, so that it is highly flexible. In order to have the desired electrical characteristics, such as matching the characteristic impedance performance with the rigid PCB it interconnects, each circuit layer of the multi-layer flexible PCB component must be designed with a signal line on the ground plane. In order to have high flexibility, a thin and suitable coating, such as polyimide, can be used on the conductor layer to replace a thick laminated coating. The metallized holes enable the z-plane between the flexible circuit layers to achieve the required interconnection. This multilayer flexible PCB is most suitable for designs requiring flexibility, high reliability and high density.
2) Multilayer PCB is formed on flexible insulating substrate, and the finished product can be flexed as specified: this kind of multilayer flexible PCB is made of flexible insulating materials, such as polyimide film, laminated into multilayer boards. Loss of inherent flexibility after lamination. When the design requires the maximum use of the insulation characteristics of the film, such as low dielectric constant, uniform thickness medium, light weight and continuous processing, this kind of soft PCB is used. For example, multilayer PCBs made of polyimide film insulation materials are about one-third lighter than epoxy glass cloth rigid PCBs.
3) Multilayer PCB is formed on soft insulating substrate, and the finished product must be able to be formed, rather than continuously flexed: such multilayer soft PCB is made of soft insulating materials. Although it is made of soft materials, due to the limitation of electrical design, for example, for the required conductor resistance, thick conductors are required, or for the required impedance or capacitance, thick insulation isolation is required between the signal layer and the ground plane. Therefore, it has been formed in the finished product application. The term "formable" is defined as: multilayer flexible PCB components have the ability to make the required shape, and can no longer be flexed in application. It is applied in the internal wiring of avionics unit. At this time, it is required that the stripline or three-dimensional space designed conductor has low resistance, minimal capacitive coupling or circuit noise, and can be smoothly bent to 90 ° at the interconnection end. Multilayer flexible PCB made of polyimide film material realizes this wiring task. Because polyimide film has high temperature resistance, flexibility, and good overall electrical and mechanical properties. In order to realize all interconnections of this component section, the routing part can be further divided into multiple multi-layer flexible circuit components, which are combined with adhesive tape to form a printed circuit bundle.
1.4 Rigid flexible multilayer PCB
This type is usually on one or two rigid PCBs, including soft PCBs that are necessary to form a whole. The soft PCB layer is laminated in a rigid multilayer PCB to meet special electrical requirements or extend to the outside of the rigid circuit, so as to replace the Z-plane circuit assembly capability. Such products have been widely used in electronic equipment that take compressing weight and volume as the key, and ensure high reliability, high-density assembly and excellent electrical characteristics.
Rigid flexible multilayer PCBs can also bond and press the ends of many single-sided or double-sided flexible PCBs together to form a rigid part, while the middle is not bonded to form a soft part. The Z-side of the rigid part is interconnected with metallized holes. flexible circuits can be laminated into rigid Multilayer boards. This kind of PCB is increasingly used in those occasions that require ultra-high package density, excellent electrical characteristics, high reliability and strict volume limitation.
A series of hybrid multilayer soft PCB components have been designed for military avionics. In these applications, weight and volume are crucial. In order to meet the specified weight and volume limits, the internal package density must be very high. In addition to high circuit density, all signal transmission lines must be shielded to minimize crosstalk and noise. If shielded separated conductors are to be used, it is practically impossible to package them into the system economically. In this way, mixed multilayer is used
Soft PCB to realize its interconnection. This component includes shielded signal lines in a flat stripline flexible PCB, which is an essential part of a rigid PCB. At a relatively high level of operation, after the manufacturing is completed, the PCB forms a 90 ° S-shaped bend, which provides a way for z plane interconnection. Under the effect of the vibration stress of x, y and z planes, the stress strain can be eliminated on the solder joint.